Get Started
Solving today’s problems for a better tomorrow.
The size, connectivity, coverage, and architecture of networks vary. This tutorial examines prevalent network types, their advantages, and use cases.
Network infrastructure size
A computer network is a collection of interconnected devices known as network nodes that exchange information, data, and resources.
Devices that connect to a network might be as basic as laptops or smartphones, depending on the sort of network. Larger networks build the underlying network infrastructure using hardware like routers and switches.
Every network is different. There are various network kinds, each of which is there to support the system’s devices, size, and location. Networks also have several sorts of connectivity and access levels.
Typical network types, together with their advantages and use cases, are listed below.
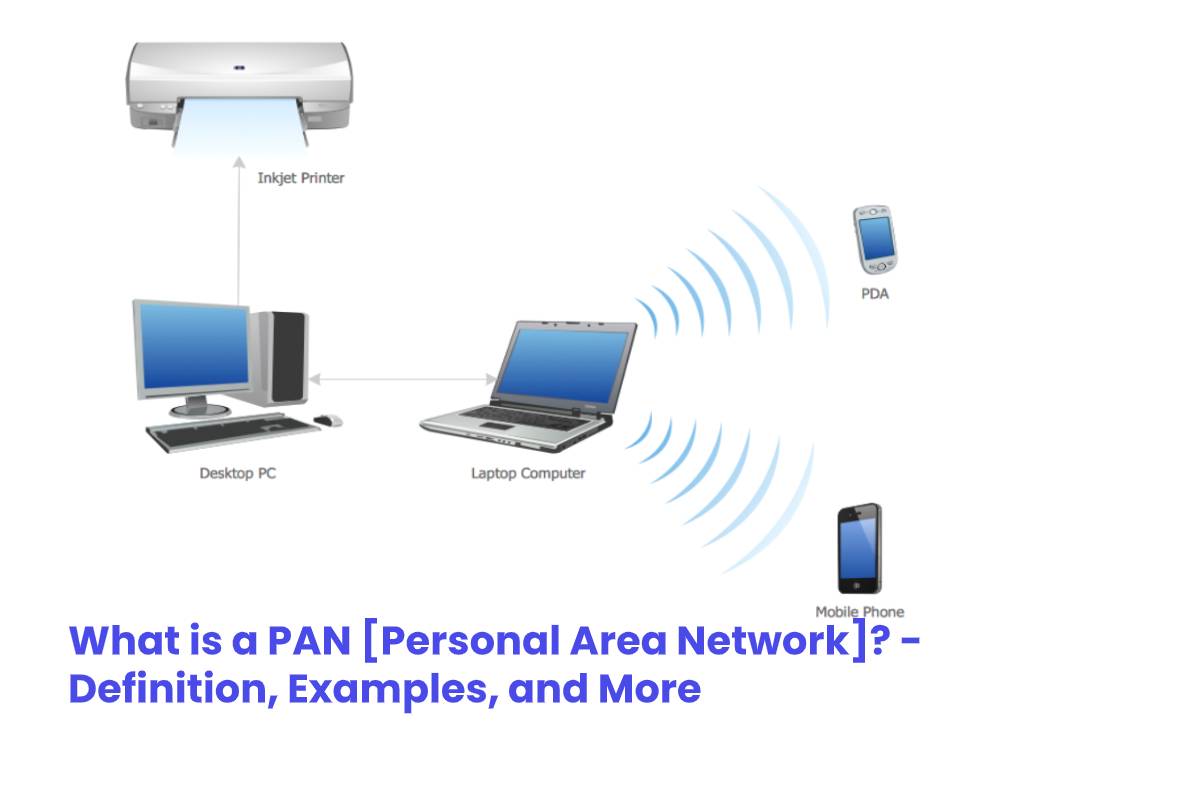
(PAN) Personal Area Network
The most basic sort of network is a personal area network (PAN). PANs, which connect devices within a person’s range and are no bigger than roughly 10 meters (m). The majority of PANs are wireless and offer short-range networking using infrared technology because they operate in such constrained amounts of space.
When users attach Bluetooth accessories to a smartphone or laptop, such as wireless headsets, they are creating a wireless PAN. Although wireless PANs predominate, there are wired PAN solutions, including USB.
PAN advantages:
Portability. The majority of the PAN-connected devices are compact and portable.
Affordability. A PAN typically costs cheaper to connect two devices than a wired network since it can do so without extra equipment.
Reliability. PANs ensure consistent connectivity between devices so long as they stay within a 10 m range of one another.
Security. PANs instead connect to other devices linked to larger networks rather than larger networks themselves. Depending on how secure the intermediary device is inside the wider overall network, a device’s security in a PAN is dependent.
PANs may play a significant role in the field of futurology in the future. PANs may be able to enhance and enable IoT systems in both homes and companies, according to several networking experts.
(VPN) Virtual Private Network
A virtual private network (VPN) envelops an existing public network with a private network. VPNs use tunneling methods to provide secure connections between client devices and the network. In order to properly conceal a user’s IP address and data from ISPs and cybersecurity hackers, network traffic is routed through secure, encrypted tunnels provided by the VPN provider rather than a public network. The location of the user seems to be wherever the VPN server is.
VPN Benefits:
Discretion and anonymity. Users can browse a network without having an ISP watch what they do.
Geo-spoofing. Geo-Spoofing Whether the server is in a corporate headquarters or a different country entirely, users connected to VPNs appear to be in the same area as the server. Outside of their country’s borders, users can access geo-restricted material or retrieve corporate data.
Improved safety. Before being able to connect to a VPN, users must first get authentication. By limiting access to sensitive data by unauthenticated users, organizations can protect firm data in this way.
An ISP can keep track of a user’s online activities, including the websites they visit and the content they download. VPNs allow users to use the network service while concealing this information from their ISP. VPNs also make it easier for people who operate remotely from places other than offices. Using VPN client software, user devices can connect to the VPN server of their company and have access to the data center of their place of business. They have the same access to the same information and resources as staff members who are physically present in the office thanks to that connection.

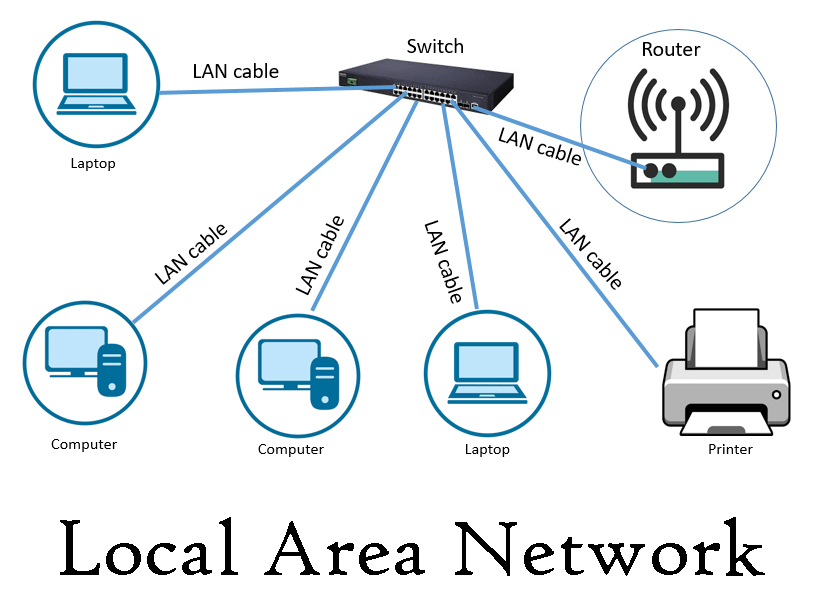
(LAN) Local Area Network
A local area network (LAN) is a system that connects computers and other devices in a single space. The range of a LAN can be anywhere from a few meters in a home to hundreds of meters in a huge corporation building, whereas PANs connect devices around an individual. The way devices in LANs are connected depends on the network topology.
Both wired and wireless networking methods are used in LANs. Although traditional wired LAN has lost ground to wireless LAN (WLAN) in terms of popularity, wired LAN is still the more dependable and secure alternative. WLANs connect network devices using hardware like wireless routers and access points rather than physical cables and switches like those used in wired LANs.
To protect wireless networks, network administrators might install security protocols and encryption standards. Because they require a physical cable to make a connection and are much less prone to compromise, wired LANs are typically more secure.
LAN advantages
Sharing of resources. One of the most crucial reasons for establishing any network is resource sharing. More files, data, and software can be shared between connected devices as more devices connect to one another.
Storing data securely. All linked devices have access to a single central place where network data is kept. Devices need authorization to connect to the network, preventing unauthorized users from accessing private data.
Quick communication. The velocity of communication between devices is accelerated by the rapid, dependable data transfer speeds offered by Ethernet cables.
continuous communication. On the same network, any authorized user can talk to another.
LAN usage examples
LANs provide a variety of network contexts, including home offices and business networks. Users at home offices can link their devices and efficiently transmit data between them. In-office staff members can easily communicate, exchange, and access the same information and services offered by their employer.
Wi-Fi is the most typical WLAN application case. Wi-Fi radio waves can be used by a wireless network to link several devices together in a single space. However, it’s crucial to remember that WLAN and Wi-Fi are not the same. A WLAN is a network that uses Wi-Fi, however not all WLANs do.
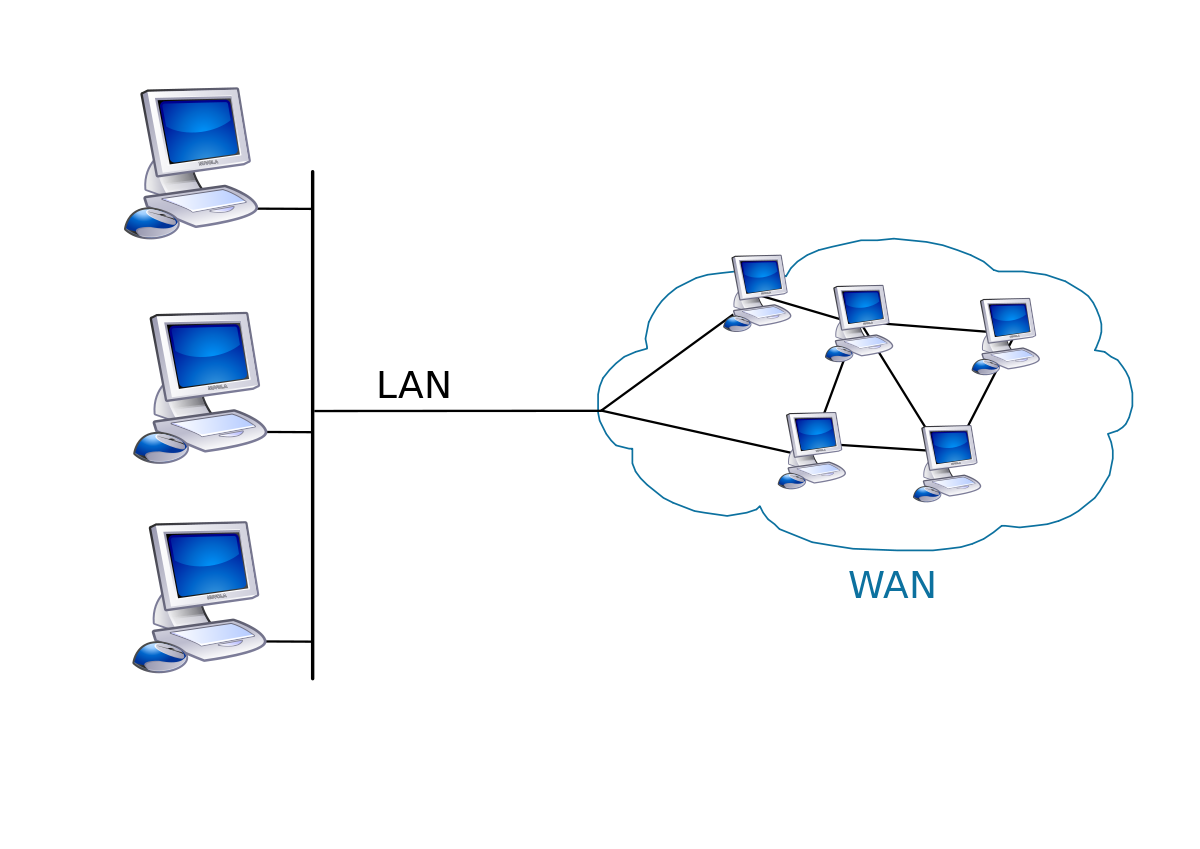
(WAN) Wide Area Network
The largest configuration of a computer network is a wide area network (WAN). Similar to a MAN, a WAN connects various LANs that are part of the same network. However, unlike MANs, WANs are not limited to the boundaries of cities. Any region of the world can be reached by a WAN. A company with a corporate office in New York, for instance, can link a branch facility in London to the same WAN. Users are able to speak with one another and have access to the same data, files, and applications in both places.
The advantages of WAN
Coverage is extensive. Because networks can connect from anywhere in the world, WANs provide more expansive connectivity.
Performance has improved. WANs connect LANs by using dedicated bandwidth links. These links improve network speeds and data transfer rates over LANs.
Enhanced security. Dedicated links also improve network security because the network only connects to itself, making it less likely for hackers to hijack a system.
WAN application scenarios
The main benefit of a WAN is that it allows for long-distance network connectivity. WANs are used by businesses to connect branch offices located far from headquarters. Businesses aren’t the only ones who can benefit from WANs; the internet, the world’s most popular and largest WAN, is used by an estimated two-thirds of the world’s population today.
Before deciding which type of network to configure, network professionals should ask a series of questions about the system. Determining the network’s use case, the types of users and devices it will serve, and the network’s location will aid in the process of selecting the network type and connectivity to deploy.
With years of experience assisting clients in the Mid West region with their Structured Cabling needs, Porthill Networks has been a dependable cabling contractor at designing and installing high-quality structured cabling systems. With Porthill Networks, you can be confident that your structured cabling installations will be completed quickly and expertly the first time around.
Are you curious in how we can support your business? Get a price for a low voltage installation (or another cabling-related service) from Porthill Networks right away.
